Measure Air quality with MQ-135 and ESP8266 Wemos D1 mini
As the MQ135 is not really suited as a CO2 sensor (See my previous blog) and I still wanted to use it, I will use it as an air quality probe on an ESP8266.
As the title mentioned I will use an ESP8266 connected to my local WiFi router for this to send the data to thingspeak.com.
The ESP8266 I use is the Wemos D1 mini. The Wemos D1 mini has an USB interface and can be programmed with the normal Arduino GUI. You can add the board to it. See this article for how to add this board to the GUI.
I also use an DHT22 (AM2302) in this project to measure temperature and 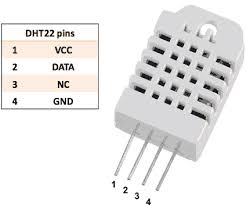 humidity. The DHT22 data pin is connected to pin D5 of the ESP8266 in my project. VCC is connected to the 5V of the ESP, GND is connected to GND. You can of course any digital pin you want in your project. Just change line “#define DHTPIN D5” with the pin number you want.
humidity. The DHT22 data pin is connected to pin D5 of the ESP8266 in my project. VCC is connected to the 5V of the ESP, GND is connected to GND. You can of course any digital pin you want in your project. Just change line “#define DHTPIN D5” with the pin number you want.
For the MQ-135 you can only connect it to pin A0, as this is the only analog pin on the ESP8266.
For the air quality I store the lowest measured value in the EEPROM, so anything worse/higher that this best value is bad air quality. I use variable a1 & a2 & a3 to check if it is an new ESP8266, if these value in EEPROM are different than the stored values I presume that it is a new ESP and then set the lowest value to 510, if the values are the same I do not change the lowest value in EEPROM.
Below the program I use for this project.
I will try to describe any main step of it.
As there are some problems copying the below text I have added download links at the bottom of this page.
// Add the ESP8266 library
#include "ESP8266WiFi.h"
// replace with your channel’s thingspeak API key
String apiKey = "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX";
const char* server = "api.thingspeak.com";
// Add the EEPROM library to store the lowest measured MQ-135 value
#include "EEPROM.h"
int address = 24;
byte value;
// DHT22 setup
#include "DHT.h"
#define DHTPIN D5
#define DHTTYPE DHT22 // DHT 22 (AM2302), AM2321
DHT dht(DHTPIN, DHTTYPE);
float val;
float vall;
int sensorPin = A0;
int sensorValue = 0;
float v;
float h; // humidity
float tc; // temperature
float tf; // temperature
float f = 0.;
float pp = 0.;
// number of analog MQ-135 samples taken each time
int s = 25;
int t;
int x;
int lowest = 500;
int lowest_l;
int lowest_h;
int tel = 0;
int telc = 0;
int id = 1;
int air;
int airt;
int airv;
// change one value below to reset lowest value back to 510
int a1 = 148;
int a2 = 231;
int a3 = 23;
// cl should be >= 3 before writing new low
// value to EEPROM
int cl = 0;
// 5 SSID's possible for when you need to measure
// at different places
const char* ssid1 = "your ssid 1";
const char* password1 = "your ssid 1 password";
const char* ssid2 = "your ssid 2";
const char* password2 = "your ssid 2 password";
const char* ssid3 = "your ssid 3";
const char* password3 = "your ssid 3 password";
const char* ssid4 = "your ssid 4";
const char* password4 = "your ssid 4 password";
const char* ssid5 = "your ssid 5";
const char* password5 = "your ssid 5 password";
// start with ssid1
const char* ssid = ssid1;
const char* password = password1;
WiFiClient client;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(57600);
EEPROM.begin(512);
pinMode(sensorPin, INPUT);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
Serial.print("Trying ");
Serial.print (ssid);
Serial.print(" - ");
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
telc = telc + 1;
if ( telc >= 10) {
if ( id == 1 ) {
ssid = ssid1;
password = password1;
id = 2;
} else {
if ( id == 2 ) {
ssid = ssid2;
password = password2;
id = 3;
} else {
if ( id == 3 ) {
ssid = ssid3;
password = password3;
id = 4;
} else {
if ( id == 4 ) {
ssid = ssid4;
password = password4;
id = 5;
} else {
if ( id == 5 ) {
ssid = ssid5;
password = password5;
id = 1;
}
}
}
}
}
telc = 0;
Serial.println(".");
Serial.print("Trying ");
Serial.print (ssid);
Serial.print(" - ");
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
}
delay(2000);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("Connected");
delay(100);
Serial.print("IP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
// check if this is new hardware to set EEPROM to 510
if (EEPROM.read(505) == a1 || EEPROM.read(506) == a2 || EEPROM.read(507) == a3) {
Serial.println ("EEPROM setup is correct, not changing current values");
} else {
// this should be a new start
EEPROM.write(500, 255);
EEPROM.write(501, 255);
EEPROM.write(505, a1);
EEPROM.write(506, a2);
EEPROM.write(507, a3);
delay(50);
EEPROM.commit();
Serial.println ("New start for MQ135, startup values set");
}
lowest_l = EEPROM.read(500);
lowest_h = EEPROM.read(501);
lowest = lowest_l + lowest_h;
dht.begin();
// sleep 10 minutes to warm up the MQ135
// 10 minutes could be to low as warmup can take longer
Serial.println("Sleep 10 minutes to warm up MQ-135");
delay(600000);
}
void loop() {
v = 0;
t = 0;
while (t < s) {
// Read the anolog value s (25) times
val = (analogRead(sensorPin)) * 1;
v = v + val;
t++;
delay(10);
}
vall = v / s;
Serial.print ("raw = ");
Serial.println (vall);
if (vall <= lowest - 1 ) { cl = cl + 1; } else { cl = 0; } // to avoid wrong low value, the value must be 3 times low if (cl >= 3) {
cl = 0;
lowest = vall;
if (lowest >= 255) {
lowest_l = 255;
lowest_h = lowest - 255;
} else {
lowest_l = lowest;
lowest_h = 0;
}
EEPROM.write(500, lowest_l);
EEPROM.write(501, lowest_h);
delay(50);
EEPROM.commit();
Serial.println ("New lowest value, saving to EEPROM");
}
vall = vall - lowest;
if (vall <= 0 ) { vall = 0; } airt = airt + vall; airv = airt / (tel + 1); Serial.print ("low: "); Serial.println (lowest); Serial.print ("Bad Air quality : "); Serial.println (vall); Serial.print ("Bad Air quality average: "); Serial.print (airv); Serial.print (" "); Serial.print (tel + 1); Serial.print (" "); Serial.println (airt); delay(4982); tel = tel + 1; if (tel >= 57) {
tel = 0;
air = airt / 57;
ReadDHT();
if (tc == 1 && h == 1) {
delay(2000);
ReadDHT();
}
if (tc == 1 && h == 1) {
delay(2000);
ReadDHT();
}
if (tc == 1 && h == 1) {
delay(2000);
ReadDHT();
}
ZendData_thingspeak();
airt = 0;
}
}
void ZendData_thingspeak() {
// I am using 4 fields at Thingspeak
// 1 = temperature
// 2 = humidity
// 3 = Air Quality
// 4 = lowest ever Air Quality
if (client.connect(server, 80)) { // "184.106.153.149" or api.thingspeak.com
String postStr = apiKey;
postStr += "&field1=";
postStr += String(tc);
postStr += "&field2=";
postStr += String(h);
postStr += "&field3=";
postStr += String(air);
postStr += "&field4=";
postStr += String(lowest);
postStr += "\r\n\r\n";
client.print("POST /update HTTP/1.1\n");
client.print("Host: api.thingspeak.com\n");
client.print("Connection: close\n");
client.print("X-THINGSPEAKAPIKEY: " + apiKey + "\n");
client.print("Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded\n");
client.print("Content-Length: ");
client.print(postStr.length());
client.print("\n\n");
client.print(postStr);
Serial.println("Data send to Thingspeak");
client.stop();
}
}
void ReadDHT() {
// Reading temperature or humidity takes about 250 milliseconds!
// Sensor readings may also be up to 2 seconds 'old' (its a very slow sensor)
h = dht.readHumidity();
// Read temperature as Celsius (the default)
tc = dht.readTemperature();
// Read temperature as Fahrenheit (isFahrenheit = true)
tf = dht.readTemperature(true);
// Check if any reads failed and exit early (to try again).
if (isnan(h) || isnan(tc) || isnan(tf)) {
Serial.println("Failed to read from DHT sensor!");
h = 1;
tc = 1;
return;
}
Serial.print("Humidity: ");
Serial.print(h, 1);
Serial.println(" %\t");
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(tc, 1);
Serial.println(" *C ");
}
If you only want to use the MQ135 without the DHT22 then use the code below.
// Add the ESP8266 library
#include "ESP8266WiFi.h"
// replace with your channel’s thingspeak API key
String apiKey = "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX";
const char* server = "api.thingspeak.com";
// Add the EEPROM library to store the lowest measured MQ-135 value
#include "EEPROM.h"
int address = 24;
byte value;
float val;
float vall;
int sensorPin = A0;
int sensorValue = 0;
float v;
float f = 0.;
float pp = 0.;
// number of analog MQ-135 samples taken each time
int s = 25;
int t;
int x;
int lowest = 500;
int lowest_l;
int lowest_h;
int tel = 0;
int telc = 0;
int id = 1;
int air;
int airt;
int airv;
// change one value below to reset lowest value back to 510
int a1 = 148;
int a2 = 231;
int a3 = 23;
// cl should be >= 3 before writing new low
// value to EEPROM
int cl = 0;
// 5 SSID's possible for when you need to measure
// at different places
const char* ssid1 = "your ssid 1";
const char* password1 = "your ssid 1 password";
const char* ssid2 = "your ssid 2";
const char* password2 = "your ssid 2 password";
const char* ssid3 = "your ssid 3";
const char* password3 = "your ssid 3 password";
const char* ssid4 = "your ssid 4";
const char* password4 = "your ssid 4 password";
const char* ssid5 = "your ssid 5";
const char* password5 = "your ssid 5 password";
const char* ssid = ssid1;
const char* password = password1;
WiFiClient client;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(57600);
EEPROM.begin(512);
pinMode(sensorPin, INPUT);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
Serial.print("Trying ");
Serial.print (ssid);
Serial.print(" - ");
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
telc = telc + 1;
if ( telc >= 10) {
if ( id == 1 ) {
ssid = ssid1;
password = password1;
id = 2;
} else {
if ( id == 2 ) {
ssid = ssid2;
password = password2;
id = 3;
} else {
if ( id == 3 ) {
ssid = ssid3;
password = password3;
id = 4;
} else {
if ( id == 4 ) {
ssid = ssid4;
password = password4;
id = 5;
} else {
if ( id == 5 ) {
ssid = ssid5;
password = password5;
id = 1;
}
}
}
}
}
telc = 0;
Serial.println(".");
Serial.print("Trying ");
Serial.print (ssid);
Serial.print(" - ");
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
}
delay(2000);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("Connected");
delay(100);
Serial.print("IP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
// check if this is new hardware to set EEPROM to 510
if (EEPROM.read(505) == a1 || EEPROM.read(506) == a2 || EEPROM.read(507) == a3) {
Serial.println ("EEPROM setup is correct, not changing current values");
} else {
// this should be a new start
EEPROM.write(500, 255);
EEPROM.write(501, 255);
EEPROM.write(505, a1);
EEPROM.write(506, a2);
EEPROM.write(507, a3);
delay(50);
EEPROM.commit();
Serial.println ("New start for MQ135, startup values set");
}
lowest_l = EEPROM.read(500);
lowest_h = EEPROM.read(501);
lowest = lowest_l + lowest_h;
// sleep 10 minutes to warm up the MQ135
// 10 minutes could be to low as warmup can take longer
Serial.println("Sleep 10 minutes to warm up MQ-135");
delay(600000);
}
void loop() {
v = 0;
t = 0;
while (t < s) {
// Read the anolog value s (25) times
val = (analogRead(sensorPin)) * 1;
v = v + val;
t++;
delay(10);
}
vall = v / s;
Serial.print ("raw = ");
Serial.println (vall);
if (vall <= lowest - 1 ) { cl = cl + 1; } else { cl = 0; } // to avoid wrong low value, the value must be 3 times low if (cl >= 3) {
cl = 0;
lowest = vall;
if (lowest >= 255) {
lowest_l = 255;
lowest_h = lowest - 255;
} else {
lowest_l = lowest;
lowest_h = 0;
}
EEPROM.write(500, lowest_l);
EEPROM.write(501, lowest_h);
delay(50);
EEPROM.commit();
Serial.println ("New lowest value, saving to EEPROM");
}
vall = vall - lowest;
if (vall <= 0 ) { vall = 0; } airt = airt + vall; airv = airt / (tel + 1); Serial.print ("low: "); Serial.println (lowest); Serial.print ("Bad Air quality : "); Serial.println (vall); Serial.print ("Bad Air quality average: "); Serial.print (airv); Serial.print (" "); Serial.print (tel + 1); Serial.print (" "); Serial.println (airt); delay(4982); tel = tel + 1; if (tel >= 57) {
tel = 0;
air = airt / 57;
ZendData_thingspeak();
airt = 0;
}
}
void ZendData_thingspeak() {
// I am using 2 fields at Thingspeak
// 1 = Air Quality
// 2 = lowest ever Air Quality
if (client.connect(server, 80)) { // "184.106.153.149" or api.thingspeak.com
String postStr = apiKey;
postStr += "&field1=";
postStr += String(air);
postStr += "&field2=";
postStr += String(lowest);
postStr += "\r\n\r\n";
client.print("POST /update HTTP/1.1\n");
client.print("Host: api.thingspeak.com\n");
client.print("Connection: close\n");
client.print("X-THINGSPEAKAPIKEY: " + apiKey + "\n");
client.print("Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded\n");
client.print("Content-Length: ");
client.print(postStr.length());
client.print("\n\n");
client.print(postStr);
Serial.println("Data send to Thingspeak");
client.stop();
}
}
Download links.
Microsoft Explorer and Microsoft Edge seems to put this on one unusable line.
But Firefox and Google Chrome are both working.